The Scythian Connection—Eastern Scotland & Ireland Share Famous Firbolg Ancestors: Create First Scythian/Scots Race
THE SCYTHIAN CONNECTION—EASTERN SCOTLAND & IRELAND SHARE FAMOUS FIRBOLG ANCESTORS who SAILED BALTIC from THRACE to GAUL— CREATED FIRST SCYTHIAN/SCOTS RACE
RECENT FORENSIC/DIGITAL IMAGERY REVEALS CELTIC GENETIC ARCHETYPE
Sailing the Baltic from Ancient Thrace, Scythian Genes reach Belgic Gaul, Eire and Caledonia
According to Irish writers, the Picts, in their first progress to Ireland from Thrace, settled a colony in Gaul, and the tribes called Pictones, Pictavi in that country are descended from them. They also gave their name to Pictavia, Poitiers and the province of Poitou. From these Picts are descended the Vendeans of France.
It would appear that the Picts were Celtic-Scythian or a mixture of Celts and other branches of the Scythian family from the Caucasus, and spoke a dialect of the Celtic language.
The Caucasus mountains synchronously create the Euro-Asian mountain divide. How revealing.



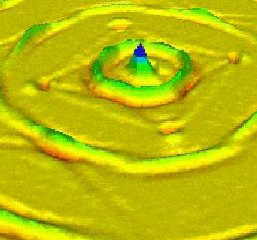
Discovered 1997 in a cave in the Black Isle, Rosemarkie Man, above left—reconstruction based on forensic digital imagery and carbon dated A.D.430-630—shows remarkable “Caucasian” Nordic &/or Hispanic features. Perhaps he arrived in a boat of skins and wood like the Broighter, right, found in a gold hoard on a Kerry beach, at the entrance to Lough Foyle. Long journey from the Baltic. Even longer from ancient homelands on the Black Sea.
The original boat would have had nine benches for the rowers, with 18 oars/rowlocks, a long oar for steering at the stern, three forked barge poles, and a grappling iron or anchor and a mast. This is the kind of boat which traded in prehistoric seas between the Channel, North Sea, Mediterranean, Baltic and west mainland Europe—Celto-Belgic, Gaulish, Brittany decor share similarities. Scythian influence had them bringing back not only goods but also ideas, technologies and fashions.
Focus of the Broighter hoard, the gold boat has ancient symbolic meaning. As centre of a rich offering to sea god Manannán macLyr, it was placed by the sea shore on a raised beach leading to Lough Foyle.
The sea was, as it still is today, an unpredictable force.
Mythical Manannán ruled his otherworldly kingdom, riding out over the waves on his chariot. He is ultimate master mariner, impervious to the sea’s deadly turbulence. Early sailors were as superstitious as their descendants! Easy to understand why open boats like this would seek his help and protection.
Along with the delight of the boat itself, the gold objects found alongside were mostly imported from the Mediterranean, including two gold neck chains from the east—possibly Roman Egypt.
Setting out from above the Arctic Circle, Scythian Celts sailed south through the Baltic in ships like the (sacred gold) Broighter Boat, above right, navigating from Archangel or St Petersburg, Lübeck, Bergen, through the North Sea, via the English Channel, Guernsey to Brittany and N. Gaul; and from the Cornish coast to W. Ireland and North to Pictland.

Caledonian chiefs were provided with wives from among widows of slain Tuatha de Danaan by Milesian monarch Eremon, so Cruithneans became “possessed of North Britain & there founded the kingdom of the Picts which continued for many centuries until 9thC when conquered by Kinneth MacAlpin, king of Dalriadic Scots-Irish colony in Scotland.” Psalter of Cashel 10thC
Class-II Pictish carved stone Monymusk, Aberdeenshire left, late cross, stylized cauldron; Reliquary original home
Akkadian Indo-Euro script, over: Akkadian Cimmerians were culturally caucasian, similar to Scythians 1000B.C.
Big Guys with Quivers of Arrows, Renowned Harpists
Belgians were called in the Gaulish-Celtic language Bolg and Bolgach, hence Firbolgs, and Firvolgians; and by Roman writers Belgae, Belgii. Celtic Bolg means ‘quiver of arrows’—apparently they were great archers, although bolgach also signifies ‘corpulent’. So, visualize large men of stout size; celebrated for their bravery. they fought with great valour against the Romans, and were called Fortissimi Gallorum by Julius Caesar, ‘most valiant of the Gauls’.
Bolgs owned a huge landmass. (Roman) Gallia Belgica covered extensive territory stretching through Gaul and northern France, including present country of Belgium. They were divided into separate tribes or nations: Parisii, Rheni, Belovaci, Atrebates, Nervii, Morini, Menapii.
Belgians were a mixed race of Cimmerians and Germans, or a Gaul-Teuton mix like Cimbrians. Having adopted neighbour Germanic language, they were sometimes considered a Gothic or Teutonic race. They were chiefly Celts or Gaels, and spoke a dialect of the Celtic language in German/Teutonic.





Every Bolg Town a Firbolg Market Town
Wealth & status were shown (above) as desirable in prehistoric and early-medieval cultural art. Mithras, god of Rome’s fascination with war and sacrifice, top left Phrygian helmet worn by honored legionaries; sacred pinnacle of Roman foot soldier’s devotion and belief. Caledonians’ sacred symbols, middle, began long before Pictish (Class I & II) incised & relief stones, with fields of Buchan littered with granite carved stone balls-all designs-c.3000B.C. In pre-Christian Scotland, early Class-I boundary stone at Drimmies, Inverurie ABD rt. in situ missing top symbol, but flowing symbol, l.below, may indicate river Don—important waterway—stone’s throw away with feet of lost ‘arch’, mirror & comb c.f. Pictish Class-I symbol chart where symbols are locally identified, e.g. horse Inverurie; bull Burghead. Last pic: Bullion Class-II relief slab Angus, approx. same vintage as battle of Nechtansmere, c.685, example of late Pictish (royal) artisan-craft smithworking community attached to a large cultural centre. Old man on horse drinking unsteadily—classic Class-II relief, no symbols but great realism, both rider & horse.
Many centuries before the Christian era, the Belgians (Bolgs) of Gaul sent colonies to Britannia. When Caesar invaded Britain, 55B.C., they were a powerful people already possessing the southern part of England from Suffolk to Devonshire. Belgic tribes in South Britain included: Cantii in Kent, Trinobantes in Essex and Middlesex; Regini and Atrebates in Surrey, Sussex, Hampshire, Berkshire, Wiltshire and Somerset; the Durotriges in Dorsetshire, and the Damnonii in Devonshire and Cornwall. Their capital city was Venta Belgarum, (trans. Bolgs’ Market; Winchester).
The Caledonians, (Picts, or Cruithneans), according to 9thC Psalter of Cashel and other ancient annals, were an Indo-European race from Scythia on borders of Europe and Asia. According to Venerable Bede, writing in 7thC Ecclesiastical History of the English People, on their flight from Thrace/Scythia through the Baltic, via Finland, they made their way over the North Sea to S.Ireland—present Bay of Wexford. Not being permitted to settle at Inver Slainge, they sailed for Albain, Scotia, “that part of North Britain now called Scotland”.
While Scotland’s Caledonia is strewn with burgh markets, fairs and summertime food festivals celebrating local specialties, equivalent Welsh, Cornish, Brittonic (Saxon-English) market towns retain their Roman character (and in places, name Venta) around which Brit agriculture and livelihood was focused: e.g. Winchester Hampshire above, Gwent-on-Wye ‘Venta’ major market S.Wales.
In an historical context, Chepstow’s Welsh name, Caes Gwent, castle of Venta, Roman ‘market place’, shows how ancient are its roots and significant its position on the confluence of the river Wye (over which the 11thC Castle of Gwent still towers) with the Severn’s great tidal estuary which eventually flows into the Bristol Channel and the Atlantic Ocean. This is southern heartland of ancient (pre-Celtic) Brythonic kingdom, where ancient Britons spoke a dialect understood by other Britons of Prydein–Roman Britannia. Their language was understood over the water-bridge in Brittany, throughout Cornwall, Isle of Man, Rheged (ancient Cumbria), Dumbarton and Strathclyde (Dun-Britton), Brigantia (Yorkshire and Northumberland) and northern Pictland (Prydein). Their ancient monuments, aligned with the movements of the heavens and dedicated to their ancestral dead, were generations older than Stonehenge. Avebury’s great circle is their nearest relative in design and in time. As are the stone balls.
Nation of Shopkeepers Come Thru with Aid when Chips are Down


Pre-Celtic waterways like great tidal Severn estuary, left, combine ancient travel route, with Roman market town, and modern shipping canal. CaerGwent=Chepstow from Roman Venta & Gaulish Brythonic Caer castle holds ancient custodianship over River Wye, Wales, & Atlantic waters
Weren’t you wondering when the Scythian connection would penetrate?
Yes, the blue&yellow flag flying over valleys between the Caucasus and the Black Sea—Ukraine. That’s where our Scythian gene comes from. That’s the cross-Caucasus Asian-Euro mix that confounds any division, brings a HUGE international so-called Caucasian alliance to front & center. You thought DNA & ancestral genealogy research were dominated by Viking-Norse? Re-think: Caucasus wins hands down.
The French—never great buddies with the English [contra the Cruithne aka 16thC Auld Alliance MQS, French court language insinuating its way into Scots]*—are reputed to be origin of uncomplimentary Brit shopkeeper comments—more likely attribution to Napoleon who really didn’t like them. Mixing metaphors here, shopping seems to have unforeseen cultural advantages in breaking barriers—like big personally-driven overseas deliveries from Bradford, Liverpool with the Euro-consortium Médecins sans frontières, and Poland and Finland loaning military equipment normally used for rescue. Shopkeepers adding groceries to growing international rescue mission for refugees score top marks for volunteering.
*Local Scots understand French imports like golf caddy (cadet, young boy), and colloquial ‘loo’ (‘gardez l’eau’) as maid throws bucket of water into Edinburgh street below—16thC—no plumbing.
Writing our Way Out of A Situation is Good (Insecure) Writers’ Cave Advice
In Ukraine, the horse is a symbol of loyalty, devotion and freedom. They still have wolf and auroch (exist in wild) symbols of fertility and strength. Crane symbolizes sadness for their native land. And they tell ancient stories of angels and dragons, like other border communities. They share mythical gods of ocean and mountains with other cultures like Brythonic Bride. Shakespeare even wrote King Lear to satisfy his craving for mythical tales of ancestral gods. Rashly, Scythians calculate Gregorian calendar now along with Western world countries celebrating Easter a month late, a dislocated Ramadan and dislodged Carnival, with a slew of social media reels to cover their trail.
A Doric Northeast Scotland (Cruithne) calendar calculation rhyme for Easter should keep us on local track with the ‘fit like’ dialect. Spoken to me at the Back o’ Bennachie, by a born-‘n’-bred Insch quine with full intonation—Picts, Scots Irish & adoptive Brit-Scythian-Thracians might like to try it.

Fit like?
‘First come Candlemas
Syne the New Meen
The niest Tiseday efter ‘at
Is aye Festern’s E’en.
That Meen oot
An’ anither at its hicht
The niest Sunday efter ‘at
Is aye Pasche richt.’
Ancient Scots Easter calculation. Anon
We in our Writer’s Cave send what we can: support comes in many guises. Gotta get out the Scythian dictionary. Or maybe, like the Doric of N.E.Scotland above Pictish throwback medieval Cruithne dialect (fit like translates as how are you); or Edinburgh’s insider French from a Parisian courtly ‘close’ [passageway], we will probably keep on keeping on.
©2022 Marian Youngblood
Solar Radiation Storms and Crossroads in Time

Erupting solar flares send spaceweather to Earth, but electromagnetic field changes also affect human temperament
Most remarkable of all is that Northern Scotland (57ºN latitude) was almost the last to be hit. Throughout November, temperatures remained a balmy 50ºF. Even (spring-flowering) gorse burst into bloom. It recalled an equally abnormal episode in April this year, where temperatures in the same corner of Scotland hit all-time highs.
Then Nature descended in spades. 160mph winds hit the Hebrides, mainland Glasgow, Clyde and central Belt, the Highlands; hurricane-force gales funneled east to hit everything not tied down — trees included. Nobody was spared.
This example of ‘freak’ weather coursing through the northern hemisphere may not be considered memorable, when the current solar cycle is through with us, but it is unusual, to say the least.
And, as we know, other consequences of seismic disturbance — earthquakes — such as the ongoing and terrible nuclear waste toxicity spreading through the Pacific ocean in the aftermath of Fukushima — are still fresh in our minds.

If Katla caldera erupts, the icemelt from its glacier would spill billions of gallons of water through Iceland's east coast into the Atlantic
Traditionally it was thought there was no connection between solar storms and terrestrial seismic activity — earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and their tendency to precipitate hurricanes, tornadoes, and wind storms round the globe. But this received wisdom is changing. Looking at the past year alone, much seems to have occurred following the Sun’s elevated status to ‘active’ (NOAA sidebar two below, right) in line for solar maximum, 2012. Solar activity in the last two months shows increasing frequency of M- and X-class flares at an alarming rate.
“I hear hurricanes ablowin’
I know the end is comin’ soon
I hear rivers overflowin’
I hear the voice of rage and ruin”
— Credence Clearwater Revival, 1969
CROSSROADS IN TIME
One of the most insightful prophecies/predictions of the Maya elders for this time is the message of change.
4 Ahau: Food scarcities. Half the katun good, half bad. The return of Kukulkan
In the 20-year period (katun) which began in 1991 and will complete in 2012, they anticipated this katun would bring ‘scarcity and the arrival of great leaders’. It is also the katun of ‘remembering knowledge and writing it down’.
In their words, we are fully immersed in a time of ‘change and conflict’. Change comes externally from weather, elecromagnetic fluctuations in the earth’s magnetic field, natural phenomena, celestial disturbance (solar flares) and trauma inflicted by others unable to stop themselves ‘exploding’ their own inner drama. Conflict stirs in the form of personal challenge, grief, bewilderment, depression, anxiety, and fear. Many are going through these experiences at this time.
The Maya (through indigenous ancestral transmission and present-day descendants) believe that it is not a time to fear. We are at a crossroads. “Now it is time to choose a new path, decide on a new Self and community direction, to venture into the unknown, to find our true identity of being”. While devotees are already flocking to this ethos in droves, others will choose to stay on the same path, console themselves with the familiar, and invest a great deal of effort in maintaining the status quo.

Photons, zero-mass light particles, (Gamma Rays), detected in space by the Fermi Space Telescope in earth orbit
Richard Feynman explains most graphically:the Nature of Nature
We on planet Earth are also electrically-charged beings. The conduit which transmits charged particles from the Sun to humans is the same conduit which steers weather through the Earth’s electromagnetic field, and into the human electromagnetic field.
Solar activity is known to influence human consciousness (from the simplest seasonal affective disorder –SAD– to extreme summer joy and productivity) and, this logically extends to the effect photons have on our human DNA.
Radiation affects the central nervous system, brain function and balance, along with human behavior, and all psycho-physical response in between. So flaring from the same star can cause us to feel nervous, anxious, jittery, dizzy, irritable, lethargic, exhausted, and suffer short-term memory lapses. We can sometimes even feel nauseous, distracted, and suffer headaches.
The Thunderbolts project encourages inter-disciplinary knowledge and collaboration of astronomers, physicists, archaeologists, mythologists and biologists bringing together understanding of previously unrelated subjects. They plan to address some of their ideas during their multi-faceted Symposium next month, January 6-8, 2012 in Las Vegas: The Electric Universe: the Human Story.
According to the Electric Universe theory as proposed by Thunderbolts scientists, solar flares and photon waves are changing the fabric of our very reality and have a powerful effect on our cells, causing our cellular memories to awaken and clear.

Veil nebula, constellation Cygnus the Swan, traditionally described as a 'cloud of ionized dust'; in Electric Universe theory seen as electromagnetic plasma filaments
‘Thunderbolts of the Gods’ David Talbott, Wallace Thornhill (2005)
“Photon energy is capable of resonating at much higher frequency than normal human emotion. It can calibrate the human system to this higher frequency, bringing consciousness into line, so that we begin to remember our soul’s purpose.”
Many believe that this speeding-up of consciousness — instant manifestation of the desired object or circumstances — is what has triggered such great interest worldwide in systems like the Law of Attraction, the Abraham-Hicks movement and the revival of New Age consciousness-raising techniques.
Photon energy connects instantly — at the speed of light — affecting all human electrical systems, most especially thought processes, so that with this new influence it is important to exercise discipline; that in expressing what we want, we practice care in not expressing what we don’t want. Or that will manifest instead. If one is in process of change and transformation, this energy works well. On the other hand, for those stuck in the past through victimization or anger, more of that will continue to manifest.
Philosopher, psychonaut and astral traveler, Terence McKenna, before he died in 2000, believed that we would become consistently and more purposefully attracted by the Eschaton — his anomalous state of ‘unknowing’, a ‘transcendental object at the End of Time’, which draws us into awareness of the ‘New’ — and that time would speed up to such an extent that in those End-days, we might be unable to experience the passage of time in the same way we did even one decade ago; indeed, compared with the concept of time of a generation, a century ago, we are already surpassing such reckoning monthly, weekly, daily. He believed this ‘Attractor’ will speed us up even more. Hence those of us aware that the phenomenon is happening are better equipped to handle the transition from ‘old human’ to New Human.
It has been suggested that, particularly during the winter months when we feel light deprivation and shortening daylight hours, we make the most of every opportunity to ‘breathe in’ available sunlight, in snatches throughout the day, in order to refuel the body’s resources. It is only twenty days until the turning of the year. Then, after solstice, the days will lengthen once more.
Before we know it 2012 will be here and with it the fulfilment of Maya prophecies: it is an exciting time to be alive — with more revelations in store.
©2011 Marian Youngblood
2009/2010 El Niño Crazies? or Just Weather
It was a dark and stormy night – oh, no – wrong genre – start again.
And amass it did.
In this neck of the woods, a white Christmas has become something of a rarity over the last score years: an event you remembered from childhood, when lampposts were short and dogs were tall; when traffic was a report you heard on the radio; when the wind blew from the North and old men predicted the white stuff. In these last few years, it feels as if the Earth is turning on the screws and testing us countryfolk to see if we’re made of the right stuff.
There’s a link there somewhere.
All summer long – I blogged about the weather, because there was nothing I could do to change it – winds brought cloud and rain from the west: dragged it kicking and screaming across the Grampian Mountains – that famous Roman chain that spawned Mons Graupius, which usually blocks precipitation – and dumped it on Aberdeenshire.
For those of you unaccustomed to our spectacular micro-climatic conditions in the Northeast triangle of Scotland, the Grampian county of Aberdeen has paleo-historically been blessed with low-level Pleistocene marine sands and gravels on its eastern coast, Devonian red sandstone on the North coast and intrusive muti-colour granites – also Devonian – in the middle. They’re the ones that usually soak up leftover raindrops.The Cairngorms form a natural divide between East and West. These stately peaks – though only in the minds of Scots, as they rise to a maximum of 4,000 feet – are geographically closer to the Atlantic Ocean than they are to the North Sea; yet their granite bloc is a block for precipitation, most years dumped unceremoniously on the long-suffering, midge-ridden West.
For every mile east you go you can expect one inch less rainfall. It’s an old Scots maxim that made some sense in Grandfather’s time.
The charmed population of Aberdeenshire has historically experienced early springs, punctual return of swallows, balmy if slightly dry summers and mild falls. Winter, since the storms of 1981-2, was a gleam in the weatherman’s eye.
Until 2009-2010.
Summer was a non-starter. A brilliant flash in late June – like a forgotten dream: one week after solstice, a few days into early July seemed like a world of childhood fantasy; running barefoot through meadow flowers, gathering domestic strawberries, wild raspberries; thinking of lush promised fruits to come: plums and pears and apples.
Then the drought (so-called ‘heat-wave’) vanished and the rains came. And with them the winds.
In the Bahamas and the Florida Keys they used to say a hurricane rhyme:‘June: too soon,
July: stand by,
August: come it must,
September: remember,
October: all over.’
It applied last year to eastern Scotland, to a scary degree.
June and July were the calm before the storm. August – a month when surprise ‘spates’ arrive and inundate fields of ripening grain, sweeping all before them into overflowing ditches, burns and rivers – brought two downpours. Central riverine communities sandbagged doors, secured and taped windows. And still it came. September there were three more floods; this time the river Don burst its banks in several places: in Kintore a farmer died in his tractor, caught out and drowned, unable to extract himself from floodwaters.
A mile of Don’s worth two of Dee
Except for fish and stone and tree
The September ‘spate’, likened to its ancestor, the ‘Muckle Spate o’ ‘29’ (by that they meant 1829), carried away everything not tied down: including fish, stone and tree.
Equinox came and went and still it rained. Still the winds blew. It was as if the hurricane season of Florida had not only exported its rhyme, but all of its storms:
After Ana, Bill and Claudette, the twisting tail headed north, skirted Bermuda and aimed straight for the north Atlantic, round the Pentland Firth and down through the Moray Firth to blast Aberdeenshire.
That’s right. Not only were these storms of gale-force strength (in high summer a wind over 60mph is unusual, to say the least), but they came from the North. Poor battered plants in struggling northern gardens usually basking in an exquisite micro-climate of Icelandic and Scandinavian temperatures, were being blown to bits.
I digress only momentarily to explain that our countryman, Admiral Sir Francis Beaufort is responsible for giving us the scale of wind speeds that we currently use. It really hasn’t changed much since he standardized it in 1806. There’s been no need. Wind, from a gentle summer breeze that cools the romantic brow (3 to 6 knots, Beaufort 2) right through to a full hurricane-force gale greater than 73mph (64 knots, Beaufort 12) has a way of letting you know it’s there.
Danny, Erika, Fred and Grace brought similar reminders: storm-force conditions injurious to plant, beast and Man. I even found a toad sheltering from the blast in a quiet niche. There seemed no let-up; no sign of a reprieve. Those of us who believed that the Earth was just playing a game, having us on, it would be Okay in another week… were in for a big surprise.I planted a giant sunflower out of its (greenhouse seeded) pot in May, thinking how lovely the vision that, in a summer like 2005, 2004, 2001 or 1998 (‘Global warming’ years) it might set seed to feed finches by autumn.
By equinox it still hadn’t flowered.
It was so statuesque, so tall, so strong – its stem larger than the area I could encompass with my two hands. It was full of moisture and had responded with phenomenal growth. But no yellow petals.
October arrived. Swallows had long departed – they’d decided for the first time in twenty years that enough was enough. They’d lingered in Ultima Thule only long enough to hatch a single clutch. They left on a singular warm wind three weeks early. I should have known then we were in for more.
I thought things would change after the ‘equinoctial gales’. It is traditionally a time when, if summer has been a little less than kind, the burgeoning vines, the bending limbs, the fully laden branches of fruit and Nature’s bounty make up for all the hard work, lost sleep, missed opportunities: the promise is fulfilled, Mother Earth comes through in spades, the sun shines and all is forgiven. The warm earth brings forth ripened plums, pears and apples in abundance, even a choice late cherry or two.
Not last year.
True, there were Granny Smiths and Cox’s Orange Pippins lying waiting on apple boughs pruned close to a sheltering wall larger than any I have ever seen. Artichokes as big as squash; squash as big as pumpkin. But I had to bring them inside to ripen or they would have moulded in the wet. Green tomatoes so abundant they were going out of style. Zucchini had been under plastic all summer, keeping out the rain. A summer too wet even for zucchini to grow! that gives you an idea of how sodden the ground was. Victoria plums which love a moist year were hanging in abundance, but they were still green, and a few delicate pears – it is a little too northerly for pears here at the best of times – looked like shrunken castanets. There was a lot of green: lettuce, cabbage, parsley and spinach to die for, but not a lot of ripening. I am not usually an ungrateful person. But my expectation was bordering on exasperation.Then suddenly, as if the weather elves had been napping and awoke in a frantic state of guilt at not having done their usual earth tending, October turned mild.
Roses bloomed, butterflies emerged from wall crevices, a dry shed, and sought out the late blossom of buddleia to stock up for overwintering. California poppies that thought they’d come to an alien planet, flowered and raised their faces to the sun.
And, lo and behold, my sunflower popped her first petal.
But the stratosphere wasn’t done yet. Not by a long shot. She’d started, so she was going to finish.
I mentioned earlier that the Grampian mountain chain forms a barrier that usually holds back rain from the West. And last year, its barricading powers failed miserably. Not only did rain follow wind and wind follow rain, but the midges, the West’s most unmentionable tourist nightmare, followed piggy-back along the trail.
The swallows, great feeders of the heavens, had already gone; so nobody was scooping great mouthfuls of the little monsters in massive numbers. Wrens, robins and a few finches that weren’t busy feeding on grain, demolished a few, but the air was alive with them. Wind seems not to perturb these tiny insects: they hide under trees and reappear the minute it drops.
So, calm evenings in the late Northeast autumn were midge-rampant; not pleasant. No window of opportunity for a leisurely stroll in the balmy, breathless air. The blackbirds had it all to themselves.Thing is, there was no evening birdsong. Most of the summer visitors had departed. And those that were still around were looking for winter habitat. Wrens can bundle together in numbers up to twenty-two in one disused nest. Body heat is the only thing that keeps out the cold. Wrens were doing a big business in re-roofing spring nests – for future reference.
There were other signs. I should have known.
Greylag geese round here have become permanent residents. They like the mild winters, so I’ve heard. They top up and home in on a familiar sheltered waterhole; they feed to stuffing point in leftover barley and wheat in open, harvested fields and then head out a little north of here to overwinter. In previous winters, winters without snow, there have been geese still tucking in in open fields in early December. This last fall, all the grain had gone by late October.
And the geese were gone too.
In late October my drenched sunflower was looking a little the worse for wear, but she was still hanging in there. Her strong stem was sturdy enough to support loads of hungry finches, tits, songbirds.
They used her as a stopping-off point between hedge and feeder-table. As if they hoped her yellow bedraggled petals would somehow unfold to present them with a miracle in fat black and white stripey seeds. It was not to be.The rain succeeded. Not in taming her, but when her petals closed in late October – usually a (midsummer) sign that the head is transfiguring, metamorphosing, setting seed – they chose not to reopen. She bowed her head and became silent. She’d had enough.
November raged and birds were blown about. Humans and animals prepared for what was to come. Early December brought some sunny days, but there was a chill in the air that nobody could really pretend was unfamiliar.
And then, one week before Christmas, the snowflakes arrived. And they fell in great soft plops of Inuit 32-linguistic varieties. And they didn’t stop falling until every last man, woman, child, blackbird, wren, robin, chicken, fox, wildcat, deer, rabbit and stoat had felt every possible chill factor they were capable of bringing.
* * *
There isn’t much point in going into the blow-by-blow of how difficult it’s been. But it might be interesting to look at the overview.
Scotland isn’t traditionally a snowy place. I’ve explained why. It sits on the northern edge of the Atlantic Ocean in a latitude akin to Alaska, but with temperatures more normal for the 42nd parallel of the Pacific Northwest. Yes, there are storms which come and go in the three months of so-called Winter, and local government services are never ready for them; it’s a standing joke. They complain before it comes, don’t deliver enough salt or grit enough or clear enough if it does and then blame central Government afterwards for not warning them or providing enough funding in the first place. As if the weather were not God’s fault, but the Labor Government’s.
People in Northeast Scotland have over time grown weary of bureaucratic bickering, complaining and infighting. In country districts in particular, they just get out and get on with it: fend for themselves. Farmers with snow-ploughs attached to tractors clear country roads which large council ploughs can no longer access.
This last winter saw more hardship, more strenuous community togetherness, more help-thy-neighbor-like-thy-life-depended-on-it gestures to make up for every snowless winter or heat-blistered summer of the new millennium.
To backtrack a little: we’ve all heard of, or been made aware of the ways of El Niño.
Spanish for ‘male child’, colloq. the Christmas Child, El Niño was the anthropomorphic name given by Peruvian sailors around 1892 to a warm northerly Pacific current in winter time. It is produced by a weather anomaly combined with atmospheric pressure: Indonesia usually experiences huge amounts of rainfall in winter under low atmospheric pressure, while high pressure hovers over the dry coast of Peru. This cycle produces a westward flow of tropical trade winds.
When the pressures weaken, the trades do too and a period of warmer-than-average sea surface temperatures arise in the east-tropical Pacific Ocean around December, blown along the surface against weakening trade winds which churn its billowing mass into a lingering ‘entity’; the length of its stay can influence weather conditions across much of the globe.
In an El Niño year, warm surface water encouraged by lessening trades migrates east from Indonesia across the central Pacific to the coast of Peru and Ecuador, bringing tropical rains which would otherwise fall on Jakarta, Bali and Papua New Guinea. Not only does the warm water linger, but with weakened winds, it forms a dense mass of warm ocean that does not sustain plankton (which prefer cooler waters) and consequently the larger fish that feed on this resource. In an El Niño year, the high desert, the Altiplano can experience huge rainstorms, while Australia and India suffer from drought.
Recent meteorological interest has been piqued by the growing frequency of El Niño years and the apparent resultant extremes in temperature worldwide which occur the following summer. El Niños since 1982 have occurred so regularly that world attention has been focused, not only on their effect on mean summer temperature but on the fact that they may contribute to ‘global warming’.
Recent El Niños happened in 1986-1987, 1991-1992, 1993-1994, 1997-1998; and in 2002-2003, 2004-2005, 2006-2007 and 2009-2010.
For comparison, using mean world temperature data, the hottest years on record are, in order of maximum extreme temperature:
1 2005, hottest on record since 1880
2 1998
3 2002
4 2003
5 2004
6 2001
7 1997
8 1990
9 1995
10 1999
These freak hot summers all happened within the last two decades. And nineteen of the hottest 20 years have occurred since 1980.
Notably, and possibly related to the gap of non-El Niño years since 2007, 2009 is not one of them!
What may be happening is that, with an erratic move away from climatic norm, weather patterns become reversed, unpredictable. Bottom line, for the weather man, a nightmare.
So back to the point. The year 2009 already marked the end of the hottest decade in history – or at least since they started measuring annual mean temperature. We are, of course eliminating Northern Scotland as a candidate here.
The winter of 2009-2010 will also go down in the history books, I suspect. Not just because Scotland was cut off from the rest of the world for virtually three months, but weather conditions everywhere were, shall we say, a little out of the ordinary.
They had frozen citrus groves in Florida in January, snow in Georgia in February; and a big freeze in northern Virginia at New Year’s. Dickey Ridge (three miles south of Dickey Holler!) had an icestorm, windchill, winds of 50mph (Beaufort 9) which took the temperature down to 8ºF – that, for the Celsius Euros among us is minus 14ºC; and that’s the Deep Saw-uth.This winter, Belgium had weather like Estonia; Estonia a brief snowfall like Guernsey. Scotland is the land of the deep freeze, British Columbia hasn’t had enough snow to support the Winter Olympics. Torrential rainfall in Sacramento, Monterey and Orange County exceeded seasonal maximum; Las Vegas had more rain in two days than in the entire previous year.
⁃ Dare one touch on other phenomena, either closely or remotely related to earth changes? After the January 12th and 13th Richter 6.5 and 7.0 earthquakes of Eureka, California and Haiti respectively, probably not; save to mention that Etna is alive again, spewing out volcanic cloud and ash, Kamchatka’s twin volcanoes are active, as are the Chilean twins of Llaima and Pichillaima in the Temuco Lake District, despite an unseasonal cap of snow! And in the Windward Island chain, the Saint Vincent volcano, La Soufrière, the Sulfurer, collapsed last week.We’re not experiencing anything out of the ordinary.
We’re just in the middle of a shakedown while Mother Earth gets herself ready for spring in the Northern Hemisphere. After all, we, her children, haven’t been behaving all that well these last two decades. So she’s entitled to shake her feathers like a tousled sea eagle and take a look round to see what else she can do to get us to pay attention. Weather is, after all, one of her mechanisms for that.
We decimate tropical rain forests, she sends less rain. We rape the desert for subterranean oil, she sends dust storms and African drought. We create huge whirlpools of plastic waste in the North Pacific Gyre trapping and killing earth’s most evolved sea mammals: it seems fitting that she should turn around and send us an oceanic anomaly to make us scratch our scientific heads in vain.
What’s in store for 2010?
If the Niño camp are right, and the winter of 2009-2010 is one of the ‘strongest’ El Niño seasons yet, then the summer which follows could outstrip all previous chart-topping statistics.
Let’s look on the bright side. Vancouver may not have had any snow to speak of, but Iowa and Idaho, Kentucky and Montana have had their fill. As has (Scotland and) the whole of the Eastern Seaboard from Virginia to Vermont: snow so deep and penetrating that the earth is going to be busy soaking it up, getting ready for new spring growth, filling riverbeds and lakes, dams and reservoirs.Snow melts down at about a 10 to 1 ratio, meaning 10 inches of snow equals about one inch of water. One thing’s for sure: we’ll have water in abundance to get us ready for the growing season.
Perhaps that’s what Mother Earth has in store. If the summer of 2010 turns out to be another like those twenty hottest years on record, maybe she’s filling up her tanks; mustering inner reserves; getting ready to take us through some punishing temperatures.
I mentioned animal signs. We humans may have lost our ability to intuit what lies ahead, but the birds, wild animals, flora and fauna know a thing or two.
Swallows left early last fall, as if they knew what was coming. The autumn bird chorus was minimal, to say the least. My few chickens stopped laying in the first week of December and, apart from one jewel of an egg that miraculously appeared (probably by accident) on Christmas Day, the little group of eight didn’t produce a single egg between them until last week. Even then, I think it was only the bright sunshine that shone warm during the day that got them motivated. They’re still pretty quick to get back inside their henhouse before five o’clock sunset. Temperatures outside right now are maintaining a solid two or three below zero.I mentioned Kamchatka. In the darkest days of solstice – and even in subsequent weeks when January turned to February and the light began to return – temperatures in this part of Scotland were, as I said, more appropriate for Siberia than for an island on the Atlantic seaboard. In the second of three storms, four blackbirds fell off their tree limbs in the night and died. I found the body of a fifth frozen under one of the vehicles, as if she hadn’t had the strength to fly for cover. A greenfinch died in my hands from sheer exhaustion and inability to get enough seed in her crop before nightfall.
As I see it, the winter of 2009/2010 has brought out the best and the worst. At the height of the storms, kind neighbors with 4×4 vehicles ferried immobile snowbound waifs to shop for emergency groceries. Birds died, but hens are laying again and there is birdsong. It’s a signal spring is on the way. The pheasant population, usually set by surrounding farmers as fodder for guns in the Spring Shoot are feeding by day with my chickens, roosting by night in my frozen trees. Safety not only in numbers, but also in the non-shooting enclave.
Aconite petals are gleaming with frost, but their yellow is trying to shine.
They remind me of my sunflower. Beaten but unbowed, she made it through some of the harshest conditions ever to greet one of the girosol family. She stood all winter, too. She stands there still. No flower, no seed, but her stem as strong as a sapling.
If she can make it through, I guess some of the rest of us will, too.
©2010 Marian Youngblood
Space Weather 30-year Storm: Earth fights back
I need hardly remind residents of Scotland that we have only just weathered the thirty-year storm. Most households living through four solid weeks of sub-zero temperatures in an Atlantic weather zone (even with the miracle of central heating) will remember this winter (and last month especially) for many years to come.Fortunately our civilization has advanced enough so that we experienced minimum electrical ‘outages’, despite heavy snow, icicles and ice on power lines. There were, however, multiple power ‘surges’ and computers countrywide were frozen in mid surge. Mac and pc-owners and related computer businesses are still counting the cost. Curry’s have been doing a roaring trade in replacement laptops!
It seems to have hit a lot of young ones harder than they might have thought: not that closing schools and cancelling bus and train services are a hazard; more time to make snowmen, play and enjoy winter sports, you might think. Lack of reliable public transportation, however – counting on any public services, in fact – four weeks without refuse collection borders on neglect, were commuters’ and householders’ concerns. Abandonment, remoteness and surprise at being cut off suddenly are what hit the teens hardest, I think because they are unaccustomed to having their social life curtailed by ‘weather’ and few had experienced conditions such as these in their young lives.
Some of us older oldies remember the winter of 1981/2 with shivering empathy; electrical failure, power cuts, snow drifts higher than houses; evacuating and rescuing neighbours, birds frozen overnight in trees. But that was back in the Thatcherite era, before the internet, when we didn’t EXPECT everything to run on time, snow ploughs to get through, petrol in cars not to freeze.
Human culture has changed in nearly 30 years: Even in the modern backwater of Aberdeenshire, the County of no motorways, the self-styled Oil Capital of Europe.
For those unfamiliar with our ways, this corner of Scotland – the Northeast triangle between Rivers Don and Dee and the balmy Moray Firth – has always flourished, but more than that, it looks after its own. Rather, I suppose, like Geordies idolizing their working-class heroes that went ‘down the pits’ or Scousers joking ‘don’t bomb Iraq; nuke Manchester’. Parochial in the extreme.Unlike some other lesser-urban metropolises, however, (Dundee, Perth, Stranraer), Aberdeen has always pulled through its hardest times: Dundee used to be known (an age ago, when the world was young) for its Jute, Jam and Journalism. Now it is home to none of these; but it has Robert Scott’s ‘Discovery‘, the Tay Bridge and it’s on the way to St. Andrews, which every golfer in the world has heard of; i.e. it participates peripherally in tourism, but some of its poorer districts are in appalling shape.
Perth floods every year and millions of national money poured in to rescue low-level housing has been a nightmare. Stranraer we won’t go into. It’s no longer on the way to anywhere.
Then there’s Aberdeen.
Perched on the westernmost limb of the North Sea’s mild Gulf Stream current, its dry climate (usually, rain from the west is captured by the Grampian mountains before it reaches the plain) and its remarkable latitude (57ºN2ºW ), akin to central Alaska, give it a climatic anomaly. Its farming hinterland was rich in Neolithic times and has grown richer.
A century and a half ago the city was hub to a thriving fishing industry; its harbours built, housed and skippered trawlers, tall clipper ships, deep sea schooners and whaling vessels. Thermopylae and Elissa were built here. Names like Alexander Hall & Sons, John Lewis and Sons, the Devanha Fishing Company sprang from everyone’s lips. As a merchant marine capital it was second only to Glasgow in Scotland and Liverpool south of the border.
Aberdeen, however, was never one to have only one egg in one basket: it was also the sole exporter of granite to needy growing urban centres: London streets were indeed paved with (Aberdeen granite) gold. Craigenlow quarry at Dunecht supplied the English capital with tons of its ‘cassies’ or granite sets – hand-cut granite blocks the size of a gingerbread loaf – to meet the demands of a city experiencing growing Victorian traffic problems. If they had but known…
At the height of Georgian expansion, Aberdeen city burghers were so wealthy, their coffers overflowing from the ocean tea trade, the Baltic route, their fishing ports supplying Europe’s tables (nowadays it’s the other way around), their granite exported the world over; that they chose to beautify: and the mile-long boulevard known as Union Street was built in 1801-05. This grandiose gesture – a feat of engineering which levelled St. Catherine’s Hill and carried the extra-wide thoroughfare across arches built over the previous lower Denburn and ancient market Green – almost bankcrupted the burghers, but brought the city fame to add to its already growing fortune.
As early as the mid-18th century, Aberdeenshire’s famous Baltic merchants continued to bring their fortunes back home; so the county continually thrived, regardless of the ups and downs of a world economy. Robert Gordon (1688-1731), founder of the Robert Gordon Hospital, now RGU, was famous for lending money made in the Danzig trade to Aberdeen businessmen who needed large working capital at even larger rates of interest. ‘Danzig Willie’ Forbes ploughed his fortune from the Baltic trade into the building of exquisite Donside château Craigievar between 1610-1625 on the family estate of Corse, when he was already landowner of Menie estate on the Belhelvie coast north of Aberdeen. John Ramsay, an Aberdeen merchant in 1758 built his palladian mansion at Straloch. Others followed suit. The county is today littered with stately Renaissance piles and Georgian mansions more appropriate to the valley of the Loire, the home counties or the wilds of Gloucestershire.Within this mix stir a couple of ancient universities – one founded in 1495, the other in 1593, both fostered and supported through the centuries by Aberdonian merchant success.
The world joke about the Aberdonian who watches his pennies is not entirely untrue. And the tradition goes back farther than the fifteenth century.
Even more relevant to the characterization, perhaps, is the fact that Aberdeen Harbour (presently run by the independent entity Aberdeen Harbour Board) is in fact the oldest running business enterprise in the United Kingdom of Great Britain, having been founded by charter signed by King David I in 1136. The business head of the kingdom resides on the edge of the North Sea.But the bell tolled. The fishing industry worldwide killed its own small fry: when container ships and tankers beheaded sailing vessels, similarly Icelandic and Norwegian refrigerated freighters signalled the death knell for trawlers and owner-operated fishing boats; and Aberdeen’s shipbuilding days were over.
In the early 1970s, Britain was experiencing the three-day-week, unemployment stats for the country were the highest then known, and even the granite industry declined. Its clients metamorphosed from those who appreciated polished stone to faceless ‘councils’ and ‘road departments’ which required the precious quartz and gneiss resource to be ground into dust-like fragments which could be mixed with tar and spread in increasing quantities on the nation’s arteries.
It looked as if Aberdeen, like every other Scots city, might founder on the rocks of history.
Then, lo and behold, along came oil. Bubbling up from below the North Sea in 1971, another industry was born. And the ‘silver city with the golden sands’ was perched on the shoreline, ready to receive it.It is said that because of its very geographic isolation the county learned to take care of itself. And its humour has a lot to do with its character.
Now that there is talk of worldwide recession and dwindling of the oil resource, the current Aberdonian humorous response is ‘oil goes out, Donald Trump comes in’. This refers to the New York entrepreneur’s £1 billion golf course resort where sand dune reinforcing work has just begun on the very landholdings of Menie once owned by Danzig Willie. Aberdeenshire is not averse to turning full circle. It has so far weathered many storms through centuries of change.
So how did we fare in this last Great Storm? How did the planet fare?
Greece had 100ºF temperatures at Christmas and Abu Dhabi and Dubai had HAIL the day before the launch of the 2,717-feet Burj Khalifa tower in the first week of January.
Scotland and Aberdeenshire in particular were at the time experiencing the grip of an Arctic winter, with traffic on all roads down to minimum and gritting and snow-ploughing said by Council spokesmen to be ‘impossible’. While they reported worries that supplies of salt from the Cheshire salt mine might be exhausted, citrus orchards throughout the state of Florida were hit by snow and frost lingered long enough to decimate their total citrus crop for 2010.
At the same time Mount Nyamulagira in a sparsely populated area of the Democratic Republic of Congo erupted, threatening an enclave of rare chimpanzees.
Eureka and Haiti had 6.5 and 7.2 Richter earthquakes respectively, while inland Northern California and Southern Oregon, usually inundated with snow, received not one drop. States of emergency were declared for Los Angeles, Orange, Riverside, San Francisco and Siskiyou counties and as the rainstorm headed east, floods swamped the Arizona desert, threatening homes and killing migrant birds. Las Vegas, Nevada had more rain in two days than for the total year of 2009 (1.69 inches). Alligators in the Everglades froze to death.
France’s Mistral blew early this year, wreaking havoc and damage to vines and vineyards in southern départements of Lyon and Provence; the Riviera harbours of St Tropez and Marseille suffered damage to private yachts.
Since the snowmelt arrived in Scotland in mid January, it is superfluous to mention that the resulting floods have routed gutters and drains in cities and country towns and overflowed ditches in outlying country areas. Perth (again) and Inverurie, Huntly and Kintore were unable to cope with the deluge. These levels of precipitation bring Aberdeen’s rainfall statistics for the year 2009 to mid January 2010 to 101.23 inches, for a county normally experiencing 33.6 inches per annum.
The Earth doesn’t like what we’ve been doing to her in the last thirty years. She’s beginning to fight back.